Fashion for Good Launches D(R)YE Factory of the Future Project
CREDIT: Fashion for Good
18 January 2022
AMSTERDAM – Today, Fashion for Good launches the D(R)YE Factory of the Future, a new consortium project that brings together several innovations in textile pre-treatment and colouration, that are set to accelerate the shift from wet to mostly dry processing. Textile processing is responsible for the highest greenhouse gas emissions, significant water and chemical use in the fashion value chain. The selected innovations have the potential to reduce emissions by up to 89%, and to cut water consumption by between 83% and 95%.
A New Consortium Project to Accelerate the Shift from Wet to Mostly Dry Processing in the Textile Supply Chain
“Textile processing is the largest contributor to carbon emissions in the supply chain and a shift to mostly dry processing is crucial for the path to net-zero. Given the interdependencies in the processing stages, a stand-alone assessment of solutions is not sufficient. By validating a combination of technologies, we can unlock the full potential of those solutions. This is why this project is so pivotal.” — Katrin Ley, Managing Director at Fashion for Good
Orchestrated by Fashion for Good, the D(R)YE Factory of the Future partners with adidas, Kering, PVH Corp., Arvind Limited, and Welspun India who bring extensive expertise in the textiles space, and innovators to bring together several novel technologies with the aim of disrupting the current processing, pre-treatment, colouration (dyeing and printing) and finishing, of textiles in the fashion supply chain. Although a number of innovations exist in this space, they are often explored in isolation. To achieve greater impact and accelerate the shift to more sustainable practices, this project, initially focuses on innovations in pre-treatment and colouration, partners several innovations together to test their solutions in combination to validate their impact and potential to scale in the fashion value chain.
Working closely with participating Fashion for Good partners and key supply chain players, eight innovators, Alchemie Technologies, Deven Supercriticals, eCO2Dye, GRINP, Indigo Mill Designs, imogo, MTIX and Stony Creek Colors, will collaborate to demonstrate innovative solutions in pre-treatment and colouration, across five different materials; cotton, polyester, blends, denim and wool. Technologies tested include plasma and laser treatments, spray dyeing, supercritical carbon dioxide (CO2) and foam dyeing. The results from the evaluations, as well as next steps for implementation, will be shared in a report in late 2022.
THE OPPORTUNITY FOR DISRUPTION
Traditional pre-treatment, colouration and finishing, which occur in Tier 2 of the supply chain (see figure below) often takes place in large tanks or baths which require vast amounts of energy, heat and water. It produces the highest amount of Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions, 52%, in addition to releasing large amounts of toxins into water. One of the key levers to reduce impact is to move from wet processes – to mostly dry processes – innovative processing technologies that require very little to no water and reduced energy1.
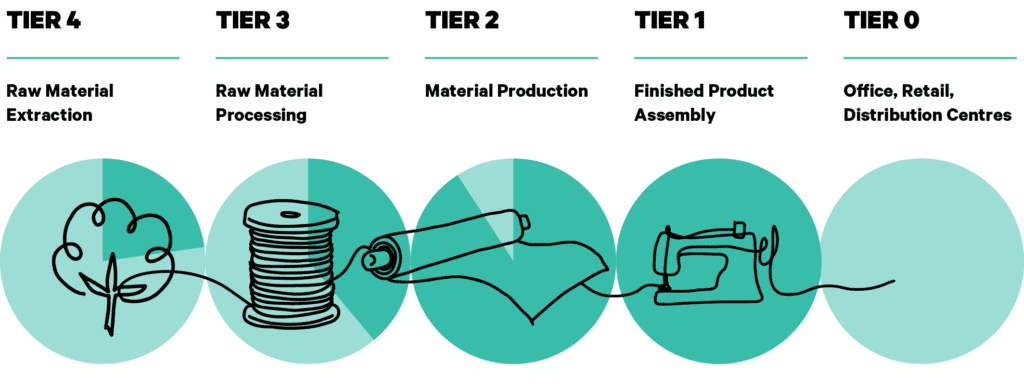
Four Tier Supply Chain Model. Source: WRI and Aii (2021)
This shift has the potential to reduce Tier 2 emissions by between 79-89% and could slash over a quarter of total GHG emissions in the industry2. An equal opportunity exists to reduce water consumption, including savings of up to 83% in pre-treatment and 95% in dyeing3.

Impact Potential of GHG Emissions in Dry Processing. Source: Fashion for Good analysis(2021)
The opportunity to accelerate this impact reduction, in this particular tier, lies in the disruptive solutions provided by participating innovators, and others emerging in this space. In comparison to conventional solutions, these technologies use little water, are effluent free, reduce the amount of consumables and as a result use less energy.
Fashion for Good has compiled an accompanying overview of these technologies and their impact potential in the “Textile Processing Guide: pre-treatment, colouration and finishing”.
NEXT STEPS
At the project close Fashion for Good will share a report with key learnings and next steps for implementation. Simultaneously, Fashion for Good will work with the participating Fashion for Good partners to help facilitate the implementation of these solutions at selected manufacturers.
The D(R)YE Factory of the Future project, also leverages the learnings and actions outlined in the recent report “Unlocking the Trillion Dollar Fashion Decarbonisation Opportunity” by Fashion for Good and Apparel Impact Institute. The report charts a trajectory for the industry to meet its net-zero ambition breaking down the funding needed and maps integral levers across existing and innovative solutions. This report identifies that the shift from wet to mostly dry processing is crucial, with the potential to abate 24% of the industry’s carbon emissions and points out a set of interventions to unlock financing and accelerate the implementation.
1. Fashion for Good and Apparel Impact Institute
2. Fashion for Good and Apparel Impact Institute
3. Fashion for Good internal analysis using innovator self reported data
Other Articles
In conversation with Smartex: Explore Smartex’s AI-driven solutions transforming quality control and reducing waste

Fashion for Good and Textile Exchange Team Up to Trace Textile Waste

